Simple Colors
Simple Colors is a subtype of coloring which only uses 2 colors.
How it works (1)
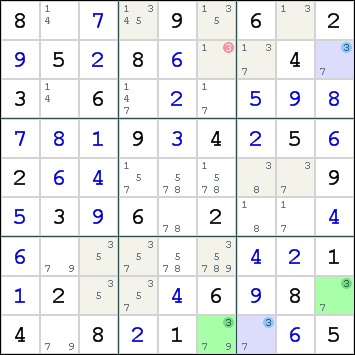
The following example demonstrates the principle:
All the candidates for digit 3 are highlighted. When a row, column or box contains only 2 candidates for a digit, one of them must be true and the other must be false. These candidates have a strong link. In coloring terminology, these candidates form a conjugate pair. We can use colors to help us remember which candidates must be true or false simultaneously. In the example, green and blue colors have been applied. Notice that row 9, column 9 and box 9 all have 2 candidates for digit 3, which now have opposite colors.
Now either all blue cells must contain digit 3 or all green cells. There is no middle ground in which some blue cells and some green cells contain digit 3.
Cell r2c6 can see both colors. It cannot sustain a candidate for digit 3.
How it works (2)
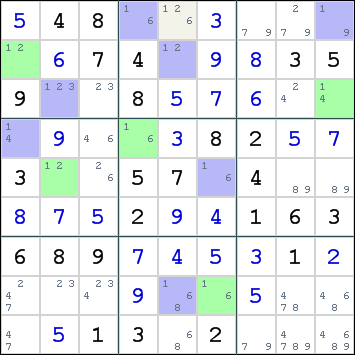
Here is an example that shows how colors can cause a contradiction.
All the candidates for digit 1 are highlighted.
Now either all blue cells must contain digit 1 or all green cells.
It is easy to see that it would be impossible for all blue cells to contain digit 1. There are 2 blue cells in row 1, box 2 and column 5. Because some blue cells are invalid, we can declare all blue cells unsuitable for digit 1.
This is the basic principle of coloring.